Welcome to the Fixler Lab at Tel Aviv University
Publications
Recent publications
Ultrasensitive optoelectronic biosensor arrays based on twisted bilayer graphene superlattice

We present an ultrasensitive, amplification-free biosensor integrating 9.4° twisted bilayer graphene (tBLG) with Au nanodisks and CRISPR-Cas12a. By aligning tBLG’s van Hove singularity with plasmonic resonance, we achieved a 7-fold photocurrent enhancement and sub-femtomolar nucleic acid detection (44.63 aM). Validated with lung cancer samples, this hybrid platform offers a scalable, real-time solution for precision diagnostics with ultralow detection limits.
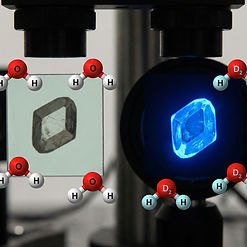
Crystallization of L-Cysteine in Heavy Water Induces Intrinsic Fluorescence
_edited.jpg)
This study shows how solvent isotopes (heavy vs. light water) drastically alter L-Cysteine crystallization, intermolecular packing, and intrinsic fluorescence. By combining experimental and electronic structure approaches, we elucidate the molecular interactions governing these changes. These findings establish design principles for new intrinsic fluorophores as novel sensing probes for biomedical applications.
Overcoming Sperm Cell Survival Challenges Cryopreserved in Nanoliter Volumes
_edited.jpg)
Cryopreserving limited sperm samples in nanoliter volumes improves recovery but causes lethal cell desiccation due to water diffusion into the surrounding oil. This study quantifies these diffusion dynamics and introduces a novel solution: using water-saturated oil to mitigate osmotic stress. By preventing water loss, this method significantly enhances sperm survival, offering a transformative approach for fertility treatments and clinical reproductive technologies.
_edited.jpg)
Anion-π Type Polymeric Nanoparticle Dispersants for Enhancing the Dispersion Stability of Organic Pigments in Water
This study introduces anion-π polymeric nanoparticles (PNPs) as high-performance, universal dispersants for water-based inkjet inks. By leveraging strong salt-bridge hydrogen bonds and π–π interactions—confirmed via FTIR and XPS—these PNPs outperform traditional dispersants in viscosity, thermal resistance, and stability. Specifically, the -PhSO3− bearing PNPs-5 yielded inks with remarkable dispersion stability and weatherability, offering a robust strategy for advancing inkjet technology.

